

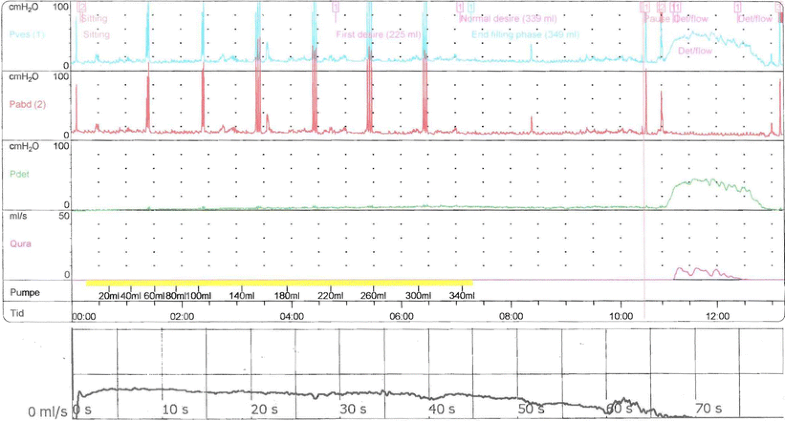
The simultaneous measurement of abdominal pressure is essential for the proper interpretation of the vesical pressure tracing. It is estimated by subtracting abdominal pressure from vesical pressure (Pdet = Pves - Pabd). In current practice, it is estimated from rectal pressure measurement.ĭetrusor pressure (Pdet) - is that component of vesical pressure that is created by forces in the bladder wall (passive and active). It is generally estimated from rectal, vaginal, or, less commonly, extra-peritoneal pressure. Intravesical pressure (Pves) - is the pressure within the bladder.Ībdominal pressure (Pabd) - is the pressure surrounding the bladder. The International Continence Society (ICS) had defined certain terms that are used in the reporting of cystometric results. It is not only the method by which the pressure/volume relationship of the bladder is measured, but it is also an interactive process that permits examination of motor and sensory function.

Cystometry (CMG) has been described as the reflex hammer of the urodynamicist. The purpose of this document is to address the various technical aspects, controversies and techniques for performing cystometry. It is also indicated in patients who have new, troublesome symptoms or complications following treatment. Further evaluation is recommended when conservative measures have failed, and invasive, potentially morbid surgical therapies are being considered. Further studies may include static voiding cystourethrography, fluorourodynamics, ultrasonography studies of the bladder and urethra, and MRI. Urodynamic assessment of bladder filling and voiding function, along with urethral pressure profilometry, is typically the first study in the evaluation of the patient with complex urinary incontinence. Despite the widespread use of cystometry, the optimal technique for performing the test is unknown. Every factor has unique implications, and before any definitive conclusions can be reached, each parameter must be examined in association with symptoms and clinical findings. It is used to assess detrusor activity, sensation, capacity, and compliance. Cystometry is an urodynamic test that measures the pressure and volume relationship of the bladder. Symptoms do not always reflect accurately the physiologic state of the bladder. To understand the fundamental value of urodynamics, one should realize that the female bladder responds similarly to a variety of pathologies.
Educational grant provided by Women's Health and Education Center (WHEC).Īn abundance of new diagnostic procedures, methodologies, and testing equipment have made it exceedingly difficult for the clinician to decide what tests are necessary to adequately evaluate lower urinary tract dysfunction in women. WHEC Practice Bulletin and Clinical Management Guidelines for healthcare providers. Women's Health and Education Center (WHEC) - Urodynamic Assessment: Techniques Urodynamic Assessment: Techniques


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
